Understanding Heroin
Heroin is a highly addictive opioid drug derived from morphine, a naturally occurring substance extracted from the seed pod of various opium poppy plants. It is known for its potent euphoric effects and significant potential for abuse and addiction.
The Nature of Heroin
Heroin, chemically known as diacetylmorphine, is often found in the form of a white or brown powder or a black sticky substance known as black tar heroin. It can be injected, snorted, or smoked, with each method delivering the drug rapidly to the brain, contributing to its high addiction potential.
Effects and Side Effects
Short-Term Effects
The short-term effects of heroin include a surge of euphoria, often referred to as a “rush,” accompanied by dry mouth, heavy feelings in the arms and legs, and a clouded mental state. These effects occur due to heroin binding to opioid receptors in the brain, which are involved in pain and reward.
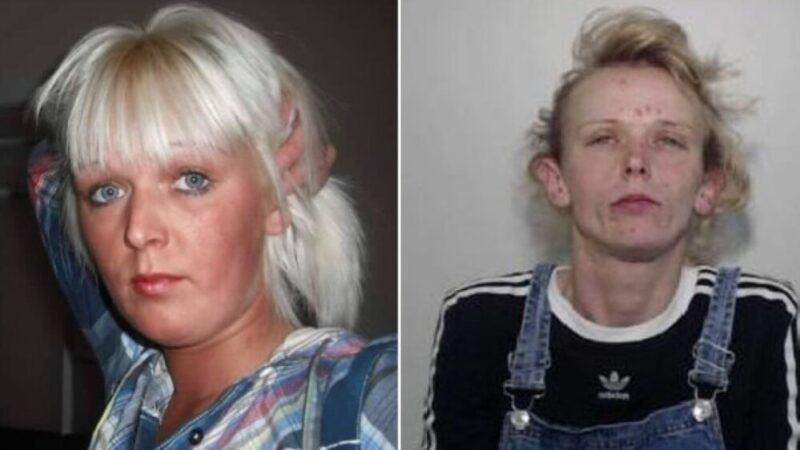

Long-Term Effects
Long-term use of heroin can lead to numerous health issues, including:
- Collapsed veins (for those who inject the drug)
- Infection of the heart lining and valves
- Liver and kidney disease
- Lung complications (such as pneumonia)
- Mental health issues (such as depression and antisocial personality disorder)
Additionally, chronic use of heroin often results in the development of tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect, and physical dependence, where the body adapts to the drug and withdrawal symptoms occur if use is reduced or stopped.
Addiction Treatment
Recognizing Heroin Addiction
Recognizing heroin addiction involves identifying both physical and behavioral signs. These include:
- Frequent use of heroin and neglect of responsibilities
- Withdrawal symptoms such as restlessness, muscle and bone pain, insomnia, diarrhea, and vomiting
- Increased tolerance requiring more of the drug to achieve the same effect
Treatment Options
Treating heroin addiction is a complex process that often involves a combination of medical and behavioral therapies.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
MAT involves the use of medications like methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone to manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. These medications help normalize brain chemistry, block the euphoric effects of opioids, and relieve physiological cravings.

Behavioral Therapies
Behavioral therapies play a crucial role in the treatment of heroin addiction. They include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): Helps patients modify their drug use expectations and behaviors and effectively manage triggers and stress.
- Contingency management: Provides motivational incentives for staying drug-free.
- Motivational interviewing: Encourages patients to develop their own motivation to change.
Rehabilitation and Support
Rehabilitation programs, both inpatient and outpatient, offer comprehensive care that includes detoxification, therapy, and support groups. Support groups such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA) provide a community of peers who share similar struggles and successes in overcoming addiction.
The Importance of Comprehensive Care
Addressing heroin addiction requires a holistic approach that combines medical treatment, psychological support, and social services. Effective treatment plans are personalized to meet the unique needs of each individual, ensuring a better chance of long-term recovery.
Preventing Relapse
Relapse prevention is a critical component of addiction treatment. Strategies include:
- Developing a strong support network of family, friends, and support groups
- Learning coping mechanisms to handle stress and triggers
- Engaging in ongoing therapy and possibly continuing medication management
Conclusion
Heroin, a powerful opioid drug, poses significant health risks and has a high potential for addiction. Understanding its effects and the complexities of treating heroin addiction is crucial for both individuals struggling with addiction and those supporting them. Through comprehensive care, including medication-assisted treatment, behavioral therapies, and robust support systems, recovery is possible.
Comments